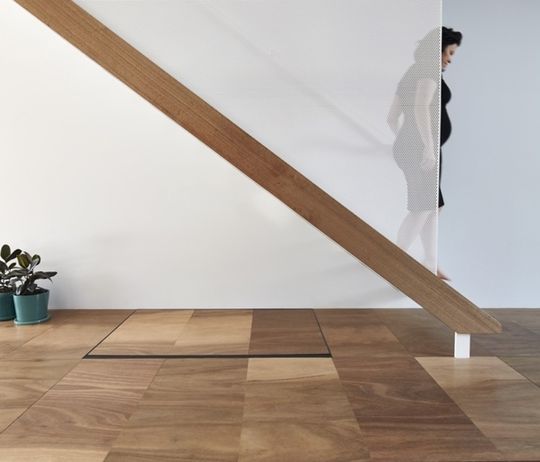
The owner of Mills House is a senior executive and now a new mum. For her and her newborn baby she wanted a light-filled home that could hide the mess. So Austin Maynard Architects (formally Andrew Maynard Architects) gave her a floor that is a giant toy-box...
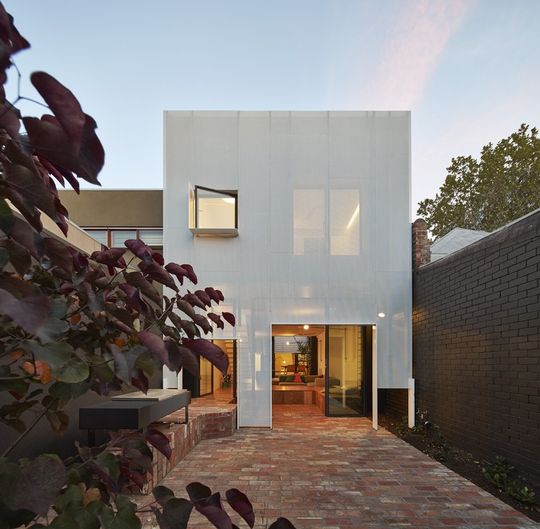


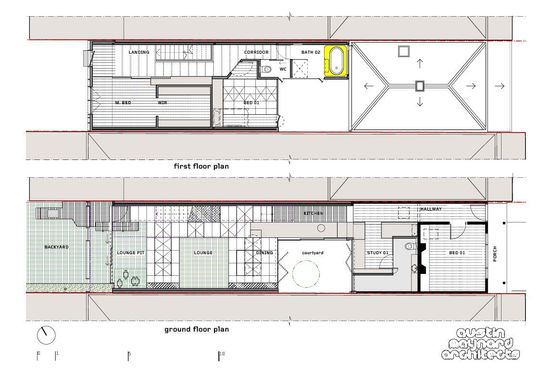
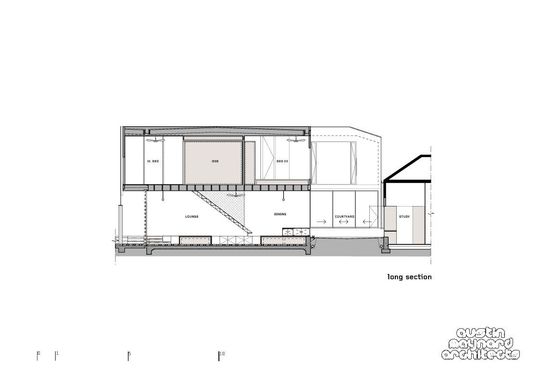
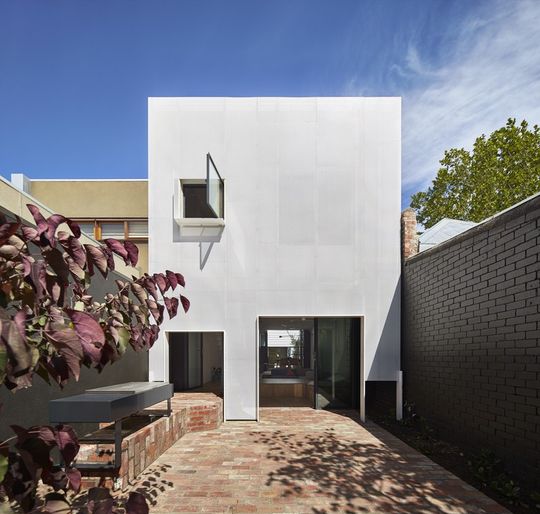
Mills House is an extension to a one level weatherboard terrace in Melbourne. The original facade and front two rooms of the terrace remain. One of those rooms has been altered to incorporate a study and a bathroom. A large light-well separates the original structure from the new extension. The extension has two bedrooms and a bathroom above an open kitchen, living, dining space.


Mills House is a complex home, full of ideas, however there are 2 core elements.
- The floor is a giant toy box.
- The rear facade filters and softens the strong sunlight that had previously dominated the back-yard.


Everyone wants an abundance of storage. Terrace homes are roughly six metres wide. After adding walls, corridors, stairs, heating panels and cupboards we are left with very little width for living space. What if we didn't have wall cupboards? We’d get almost one metre of space back into the width of our terraces. What if our storage space was within our floor? Floor space is often left to the mice and spiders. Let’s convert the floor into storage space and make the living area as big as possible without lining the walls with bulky cupboards.


At Mills House the architects have made gravity the parents’ ally rather than the child’s by enabling the floor to swallow all the mess. Rather than picking toys up to put back in the toy box, they've made the floor one big toy box. Just get a broom and sweep all the lego in from the top and sides. It becomes a game for the child as well as a new hiding place to play.


The real beauty of the toy-box floor is its height - 450 millimetres. A typical seat is roughly 450 millimetres high. The open floor is not only storage space, it is also play space at a comfortable seat height for adults. A kitchen bench is roughly 900 millimetres. Therefore a kitchen bench is two seats high. The kitchen sits on the original floor height therefore the bench is 450 millimetres above the new toy-box floor. The kitchen bench is a seat to the new floor. The architects upholstered a seat under a flap on the kitchen bench so that there can be one extra seat at the dining table when visitors are over, or when Louis wants to cook with Mum. Furthermore, the light-well garden is at the new floor height, 450 lower than the benchtop, which makes access to the herbs very easy. 450 is the magic number.


Corridors are wasted space. Austin Maynard Architects like to give corridors dual functions. The kitchen at Mills House occupies the original corridor space. Therefore the substantial space the kitchen would have occupied in a typical location has been used as living space. Upstairs the master bedroom wall can slide entirely away so that the room can increase almost two metres in length when open to the corridor. Clever ideas for small spaces.


Perforated metal is used throughout Mills House. Traditionally stairs are tricky, especially in tight spaces. But the stair in this home feels light, like lace, which is difficult considering the constant live loads a stair is under. Perforated steel sheet is folded allowing light to be shared while also enabling conversations from one level to the other, without requiring you to be in the same space. One can lounge by a sunny upstairs window while having a conversation with someone below. Although it is a small home with numerous spaces, it avoids creating isolated cells by using translucent materials like perforated metal.


Perforated metal is also used to control sunlight. We all want an abundance of sun in our homes, however too much sunlight makes any home very uncomfortable. The rear facade of Mills House faces North-West, therefore it gets hit with the most aggressive sunlight of the day. Before the renovation the owner had felt very uncomfortable at the rear of her house. A new white perforated metal facade drapes down the face of the rear elevation. The facade reflects most of the unwanted sunlight in summer, allowing a soft filtered light to penetrate the house. The lines between inside and outside have been blurred. The glass walls of the living space are offset from the perforated facade which creates a comfortable outdoor space that feels as though it is within the skin of the house. The facade feels solid and protective on a bright, hot day. On a dull day, at dusk and in the evening the facade appears far less solid and the metal skin feels more like lace than a wall.


The bathroom is not big, but the architects have created very large windows towards the light-well and towards the original roof. This makes the bathroom seem large, sunny and bright.


Adding the the sense of sun and light in the bathroom is that bathtub. No one likes cleaning a bathroom. Adding a bathtub to a small space creates a lot of fiddly details where grime, mess and mould can gather. To avoid the mess, and to create a bathroom that was easy to maintain, they architects made their own bathtub out of fibreglass. There are no seams or joins. Along the walls, a slim, continuous gutter ensures water runs around the bath and drains through the floor. Simple, neat and clean.


Like all of Austin Maynard Architects' buildings, sustainability is at the core of Mills House. Although the site is small natural light and air to all spaces has been maximised, making a big difference to the quality of space. The openings and windows have been designed to optimise passive solar gain, thereby drastically reducing demands on mechanical heating and cooling. All windows are double glazed. White roofs reduce urban heat sink and heat transfer internally. The need for air-conditioning is eliminated through active management of shade, and passive ventilation.

A large water tank has been buried central within the light-well. All roof water is captured and reused to flush toilets and water the garden. High performance insulation is everywhere, even in the walls of the original house. Where possible the architects sourced local trades, materials and fittings. Solar panels with micro-inverters cover the new roof.